What Is SEO? A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners

Everyone wants their website to show up on the first page of Google search results, right? After all, hardly anyone clicks through to the second page. So, how can you make sure your site stands out and ranks higher? The answer is simple: SEO (Search Engine Optimization). With the right SEO strategies, you can boost your visibility, attract more visitors, and increase conversions. Curious to know how it works? Keep reading this blog to explore the basics of SEO and how you can implement it for your website.
What is SEO?
The first question that comes to mind is: What exactly is SEO? You’ve probably heard marketing professionals say that every website needs SEO to increase traffic and drive sales.
From a marketing perspective, the logic is simple - the more people who visit your site, whether intentionally or by chance, the higher the chances they’ll explore your products or services and eventually make a purchase. But the real challenge is: how do we attract those visitors in the first place? That’s where SEO comes in. Search Engine Optimization helps your website get discovered, ensuring more people find and visit your site.
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It’s the process of improving your website so it ranks higher on search engine results pages (SERPs).
For example, if you search for the word ‘car’ on Google, the search engine will show results such as car dealers, manufacturers, and related content. Most users naturally click the first few links they see, and only a small percentage move on to the second or third page. This is why ranking at the top matters — SEO helps your website appear among those top results.
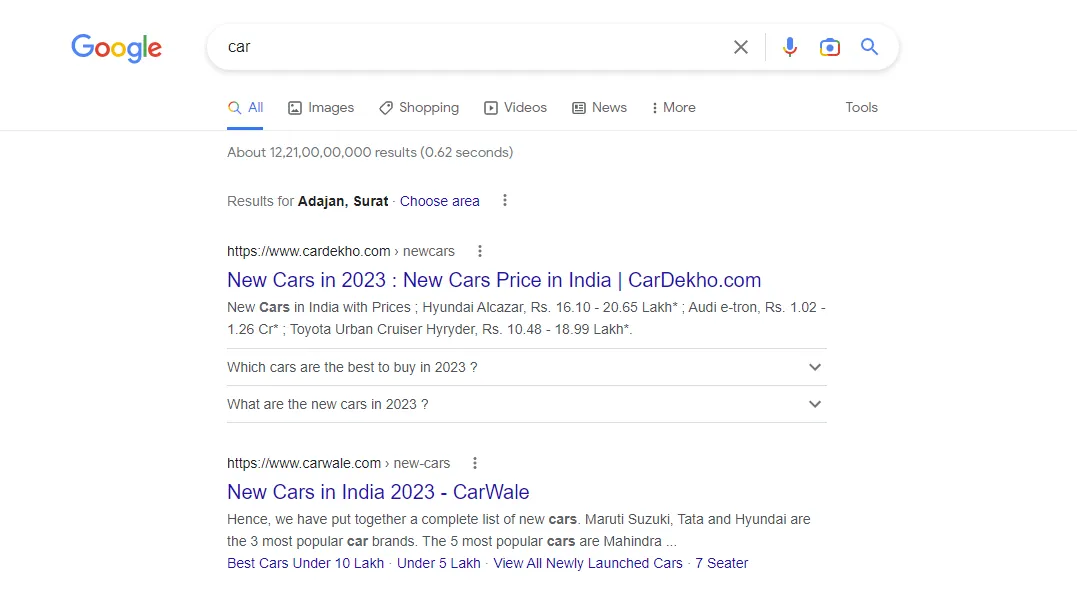
You might then wonder how Google decides the ranking of websites. That’s where SEO comes into play—it helps optimize your site so it appears higher on search engine result pages.
How does SEO works?
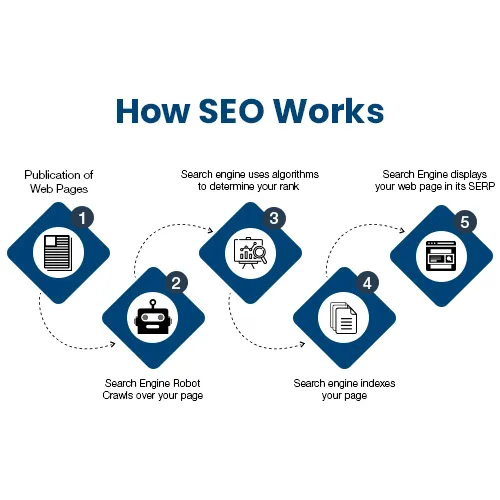
The next question is: How does SEO actually work to rank a website in search results? The process is fairly straightforward. When you provide information on your website, search engines crawl your pages, analyze the content, and store it in their database through a process called indexing.
When someone searches for a phrase, the search engine checks its database to find the most relevant results. If your content matches those search terms and is optimized properly, your website appears in the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) with a ranking based on content relevance and quality.
What is content relevance?
Every web page contains certain information such as a title, a description, and unique keywords that describe the product, service, or topic. In the case of an article, it may also include details like the author or owner. In simple terms, content relevance is all about how well your content is written, structured, and aligned with what people are searching for.
Examples of basic information include:
- Title
- Description
- Keywords
- Author or Owner (for example, an article usually has an author)”

“The most important thing to understand is that ranking doesn’t depend only on having this information — it depends on how strong and relevant that information is. Your content should clearly describe your product or service in a way that matches what people are searching for. If someone enters a related query, your site has a higher chance of appearing in the results when your content includes a clear description and well-chosen keywords that accurately represent your offering.
How to Add Information to our site?
We know that every website contains a lot of information. But how does a search engine identify which parts of that information are most important and should be used for indexing?
The answer lies in meta tags. Just like every website is built with HTML elements such as
Think of it like a shopping mall: every product has a label that lists its name, description, instructions, and price. Similarly, meta tags act as labels for your website, providing search engines with key details about your content—such as its title, description, and keywords. This helps search engines understand what your site is about and how to rank it in search results.

Meta tags define the metadata of a web page and are always placed inside the
Search engines fetch details directly from these meta tags. Each meta tag typically has two parts: a name attribute and a content value. For example:
<meta name="title" content="SEO Blog" />
- name → specifies the type of information (e.g., title, description, keywords).
- content → holds the actual value for that attribute.
There are many types of meta tags. Some are basic and commonly used—like title, description, and keywords—while others are application-specific. For example, Open Graph tags (created by Facebook) make it easier for platforms like social media apps to read and display your website information in a structured way.
i.e.
<meta name="og:title" content="SEO Blog" />
One important thing to note is that some crawlers may not fetch meta tags if they appear too late within the
This is how we add information to our site using meta tags. A complete list of useful meta tags is included at the end of this blog.
How does a search engine know which pages to crawl and which to ignore?
Most websites include sections like admin panels or management dashboards that are not meant for public access and should not be indexed by search engines. To control this, we use two essential files that guide search engines in understanding and indexing a website properly:
- sitemap.xmlThe sitemap is like a shopping list for search engines. It contains all the important pages of your site along with their URLs, priorities, and last modified dates. This helps search engines crawl your website efficiently and keep their results up to date.
Example: https://www.google.com/sitemap.xml
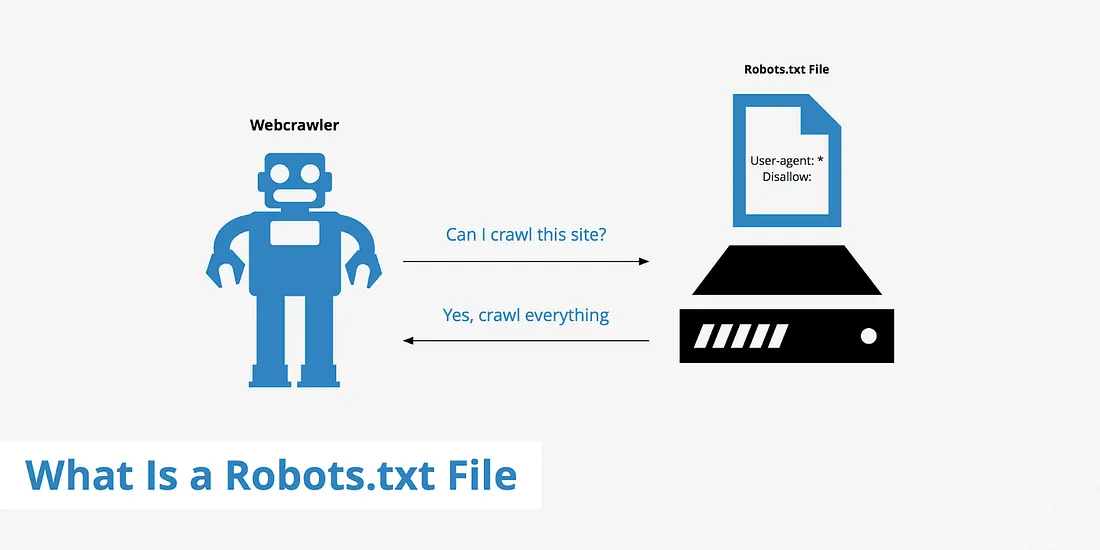
Documentation: https://www.sitemaps.org/protocol.html - robots.txtThe robots.txt file acts like instructions to search engines, telling them which pages or sections of your site should not be crawled. For example, you might allow crawling for product pages but block admin or private pages.
Example: https://www.google.com/robots.txt
Documentation: https://www.robotstxt.org/robotstxt.html
How does a search engine know that your website exists and needs to be crawled?
The answer is simple—you need to let the search engine know. To do this, you submit your website to the search console of the search engine you want to appear on. For example, with Google, you can add your site to Google Search Console.
Once submitted, Google will crawl your website, index its pages, and, over time, display it in search results—provided your content is optimized with proper keywords and strong meta tags.
https://search.google.com/search-console/about
That’s it! These are the basics of SEO. By applying these steps, you can make your website visible on search engines and start attracting organic traffic. Of course, this is just the beginning—there are many more advanced tools and strategies available to further strengthen your SEO.
Thank you for reading, and happy optimizing!
Basic HTML Meta Tags
<meta charset='UTF-8'> <meta name='keywords' content='your, tags'> <meta name='description' content='150 words'> <meta name='subject' content='your website's subject'> <meta name='copyright' content='company name'> <meta name='language' content='ES'> <meta name='robots' content='index,follow'> <meta name='revised' content='Sunday, July 18th, 2010, 5:15 pm'> <meta name='abstract' content=''> <meta name='topic' content=''> <meta name='summary' content=''> <meta name='Classification' content='Business'> <meta name='author' content='name, email@hotmail.com'> <meta name='designer' content=''> <meta name='reply-to' content='email@hotmail.com'> <meta name='owner' content=''> <meta name='url' content='http://www.websiteaddrress.com'> <meta name='identifier-URL' content='http://www.websiteaddress.com'> <meta name='directory' content='submission'> <meta name='pagename' content='jQuery Tools, Tutorials and Resources - O'Reilly Media'> <meta name='category' content=''> <meta name='coverage' content='Worldwide'> <meta name='distribution' content='Global'> <meta name='rating' content='General'> <meta name='revisit-after' content='7 days'> <meta name='subtitle' content='This is my subtitle'> <meta name='target' content='all'> <meta name='HandheldFriendly' content='True'> <meta name='MobileOptimized' content='320'> <meta name='date' content='Sep. 27, 2010'> <meta name='search_date' content='2010–09–27'> <meta name='DC.title' content='Unstoppable Robot Ninja'> <meta name='ResourceLoaderDynamicStyles' content=''> <meta name='medium' content='blog'> <meta name='syndication-source' content='https://mashable.com/2008/12/24/free-brand-monitoring-tools/'> <meta name='original-source' content='https://mashable.com/2008/12/24/free-brand-monitoring-tools/'> <meta name='verify-v1' content='dV1r/ZJJdDEI++fKJ6iDEl6o+TMNtSu0kv18ONeqM0I='> <meta name='y_key' content='1e39c508e0d87750'> <meta name='pageKey' content='guest-home'> <meta itemprop='name' content='jQTouch'> <meta http-equiv='Expires' content='0'> <meta http-equiv='Pragma' content='no-cache'> <meta http-equiv='Cache-Control' content='no-cache'> <meta http-equiv='imagetoolbar' content='no'> <meta http-equiv='x-dns-prefetch-control' content='off'>
Create Custom Meta Tags
You can use custom meta tags to store data that your JavaScript code needs, instead of hard-coding the values directly into the script. For example, I store my Google Analytics code in meta tags. Here are some examples:
<meta name='google-analytics' content='1-AHFKALJ'> <meta name='disqus' content='abcdefg'> <meta name='uservoice' content='asdfasdf'> <meta name='mixpanel' content='asdfasdf'>